What is WDA Testing?
The background for Wear Debris Analysis techniques commenced some 30 years back when Monash University pioneered a system for fine metallic contamination removal from used lubricating oil samples enabling the Wear Debris to be identified using an industrial microscope. The morphology of the wear particle identifies the abnormal wear mode that caused the defoliation of the metallic wear debris.
Wear Debris Analysis and Analytical Ferrography can be viewed as the oil analysis equivalent of CSI forensic science for machinery’s wear modes providing accurate information on the condition for used lubricants and the equipment the oil or grease sample came from.
The test methods utilises visual, microscopic evaluation of particles extracted with various filter types and magnetic separation with the contamination removed from the lubricant deposited upon a microscope slide called a Filtergram or a Ferrogram with magnetic separation.
Wear Debris Analysis is an accurate tool for identifying whether machinery is operating in a normal or abnormal wear mode. The analysis of the morphology of the wear particles generated at the commencement of abnormal wear modes accurately identifies whether it is gears or bearings creating the wear debris, plus WDA identifies the abnormal wear mode prevalent in the plant item sampled.
The information WDA provided permits rapid corrective action of the abnormal wear detected long before any permanent damage is caused that could cause downtime and requiring mechanical repair to rectify. Wear debris Analysis’ ability to detect microscopic changes to the wear debris generated by machines and wear modes in force enable WDA to usually detected abnormal wear 3-6 months before Vibration Analysis & 4-8 months before spectrographic analysis. When Vibration Analysis (VA) is combined with WDA the information provided to the plant owner is the abnormal wear mode in force, the severity of wear plus VA will accurately identify what component is wearing in the machine sampled.
Wear Debris Analysis reports provide a clear picture of the equipment’s current wear mode, possible wear causes and best corrective action. The end goal being to assist maintenance engineers in providing the maximum equipment availability at the lowest possible cost. R&T uses Wear Debris Analysis as one of their fundamental tools for evaluating used oil and or grease samples to monitor and improve the company’s overall reliability maintenance.
R&T has continually tested, developed and refined the original Wear Debris Analysis Techniques over the past 20 years until this point in time where R&T has a repeatable proprietary system that has proven to be 100% reliable. When bringing whole sections of manufacturing plants back to a normal wear mode at a low rate of wear, WDA oil analysis is the most efficient system time wise and for the amount work performed and analysis costs.
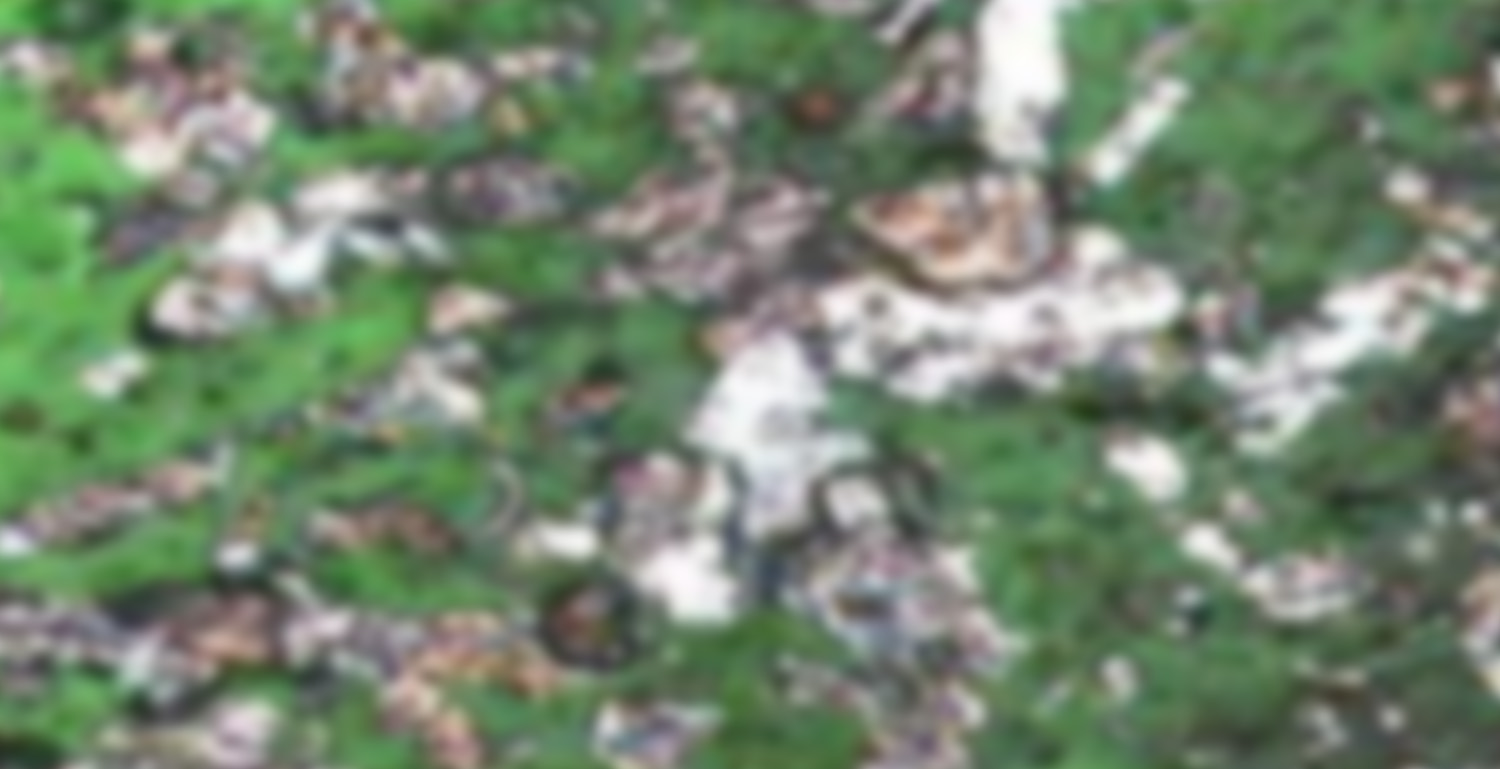
 Abnormal Wear Modes taken at 500X Mag
Abnormal Wear Modes taken at 500X Mag ![]() 20µm
20µm
 Normal Wear Modes taken at 500X Mag
Normal Wear Modes taken at 500X Mag ![]() 20µm
20µm
Using Wear Debris Analysis R&T’s experienced analysts is capable of detecting active machine wear and provide a “root cause” conclusion based on the morphology of the wear particles.
Monitoring Large Continuous Manufacturing Plants with WDA
When monitoring large continuous manufacturing plants by WDA accurate judgements can be made on whether it is worthwhile performing any maintenance steps enabling all normal wearing plants items to be screened out. If any abnormally wearing plant items are detected the WDA results diagnose the root cause of the wear and the recommendations will be to remove the root cause of the abnormality detected returning the plant item tested back to normal wear and preventing any further recurrence of the same abnormality.
Oil Sample by WDA testing provides fast accurate analysis results for when;
- Abnormal results from oil testing or vibration analysis are noted,
- Operational temperature increases or elevations in running noise is detected
- Visible metal particles are seen in oil samples, grease samples or filters.
- Escalation in Particle Counts,
- Escalation in PQ Indexes,
- Escalation in operating temperature,
- Abnormal wear commencement in drives, transmissions, hydraulics and engines
- Root cause of wear preventing wear failures in drives, transmissions, hydraulics and engines
- The component(s) that are wearing in drives, transmissions, hydraulics and engines
- Lubricant condition and suitability of running lubricants beyond their rated life
- With blowers and compressors, the efficiency and condition of main induction filters
- With combustion engines quality of combustion and efficiency of main induction filters
 |
 |
